
Welcome to the nutritional calcium content in 8 different types of zucchini, ranging from 21.00 mg to 16.00 mg per 100g. The basic type of zucchini is Squash, zucchini, baby, raw, where the amount of calcium in 100g is 21.00 mg. 21.00 mg of calcium per 100g, from Squash, zucchini, baby, raw corresponds to 2% of the calcium RDA. For a typical serving size of 1.000 large (or 16.00 g) the amount of Calcium is 3.36 mg. This corresponds to an RDA percentage of 0%.
The percentage of the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for calcium is based on a 1000 mg RDA level for a mature adult.
Top five zucchini products high in calcium
Below is a summary list for the top five zucchini items ranked by the amount or level of calcium in 100g.
1. Squash, zucchini, baby, raw : 21.00mg (2%RDA)
2. Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt : 18.00mg (2%RDA)
3. Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, frozen, unprepared : 18.00mg (2%RDA)
4. Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt : 18.00mg (2%RDA)
5. Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt : 17.00mg (2%RDA)
Following on from the five top zucchini items or products containing calcium we have a more comprehensive break down of Squash, zucchini, baby, raw, and the highest item containing calcium which is Squash, zucchini, baby, raw. We also give a comparison of average values, median values and lowest values along with a comparison with other food groups and assess the effects of storage and preparation on the 8 types of zucchini.
At the bottom of the page is the full list for the 8 different types of zucchini based on the content in different servings in grams and oz (and other serving sizes), providing a comprehensive analysis of the calcium content in zucchini.
Squash, zucchini, baby, raw - Nutritional Content and Chart
The full nutrition content, RDA percentages and levels for Squash, zucchini, baby, raw should be considered along with the calcium content. This food profile is part of our list of food and drinks under the general group Vegetables and Vegetable Products.Other important and calcium related nutrients are Energy, Protein, Total Fat and Carbohydrate. For this 100g serving in your diet, the amount of Energy is 21.00 kcal (1% RDA), the amount of Protein is 2.71 g (5% RDA), the amount of Total Fat is 0.40 g (1% RDA) and the amount of Carbohydrate is 3.11 g (2% RDA). The nutritional content and facts for 100g, which includes Energy, Protein, Total Fat and Carbohydrate is shown in the RDA chart below as percentages of the recommended daily allowance along with the calcium levels in zucchini.
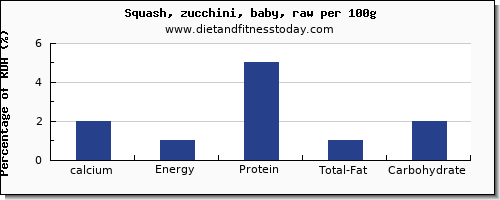
Our proprietary nutritional density score gives a nutritional value out of 100 based on 9 different vitamins, minerals and macro nutrients. Squash, zucchini, baby, raw has a nutritional value score of 36.00 out of 100.Comparing the calcium content and the nutritional density in 100g for Squash, zucchini, baby, raw; We class this as a medium to low calcium content item.In terms of overall nutritional value we class this as an item with a high nutritional density value.
Amount of calcium per 100 Calories
100 calories of squash, zucchini, baby, raw is a serving size of 0 g, and the amount of Calcium is 0 mg (0% RDA). Other important and related nutrients and macronutrients such as Total Fat, in 100 Calories are as follows; Energy 0 kcal (0% RDA), Protein 0 g (0% RDA), Total Fat 0 g (0% RDA), Carbohydrate 0 g (0% RDA). This is shown in the calcium RDA percentage chart below, based on 100 Calories, along with the other important nutrients and macro nutrients.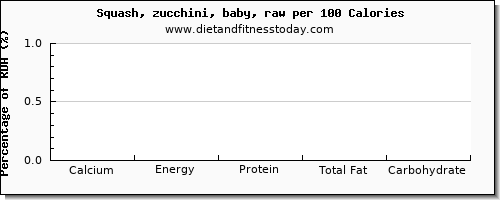
Content per Typical Serving Size 1.000 large (or 16.00 g)
For the food Squash, zucchini, baby, raw the typical serving size is 1.000 large (or 16.00 g) which contains 3.36 mg of Calcium. In terms of the gram weight and total content for this serving the Energy content is 3.36 kcal, the Protein content is 0.43 g, the Total Fat content is 0.06 g and the Carbohydrate content is 0.5 g. The percentages are shown below in the calcium chart, for the typical serving of calcium and the related and important nutritional values.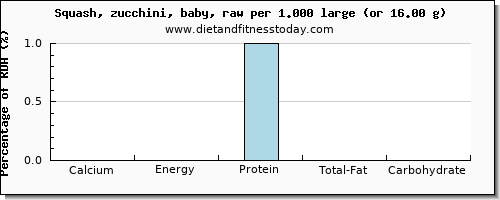
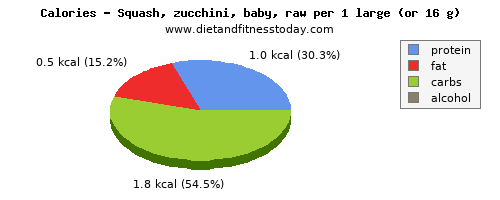
Macronutrients in Squash, zucchini, baby, raw
The amount of protein, fat and carbs from this food described above is measured in grams per 100g and grams in a typical serving size (in this case 1.000 large or 16.00 g), although it is also useful to give the number of calories from protein, fat and carbohydrate which are the most important macronutrients. For this serving in your diet here are the macronutrient calories. From protein the number of calories is 1.0 (kcal).The total calories from carbohydrate is 1.8 (kcal).
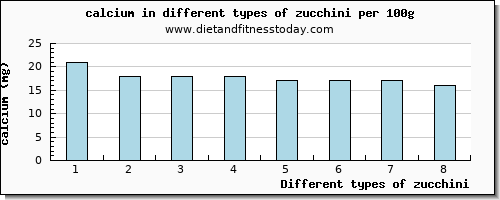
Milligrams of calcium in zucchini (per 100g)
This list of 8 types of zucchini, is brought to you by www.dietandfitnesstoday.com and ranges from Squash, zucchini, baby, raw through to Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, raw where all food items are ranked by the content or amount per 100g. The nutritional calcium content can be scaled by the amount in grams, oz or typical serving sizes. Simply click on a food item or beverage from the list at the bottom of the page to give a full dietary nutritional breakdown to answer the question how much calcium in zucchini.
The list below gives the total calcium content in the 8 items from the general description 'zucchini' each of which show the calcium amount as well as Energy, Protein, Total Fat and Carbohydrate. Below, is the top 8 food items shown in the calcium chart. This gives a quick and easy dietary comparison for the different items, where each item is listed at the bottom of the page with a nutritional summary.
The corresponding nutritional value for zucchini based on our density score out of 100 (ranked by the amount of calcium per 100g) is shown in the below nutritional density chart. 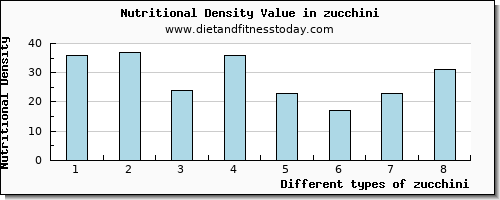
The corresponding Calories for zucchini ranked by the amount of calcium per 100g is shown below in the zucchini calories chart. 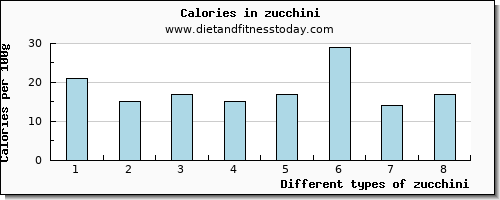
Effect of Preparation and Storage on calcium
The level of calcium can be affected by the method of storage for example canned or frozen and also by the method of preparation for example either raw, cooked or fried. The total number of frozen food items is 3. The highest amount of calcium from the 3 frozen items is in Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, frozen, unprepared where the calcium content is 18.00 mg per 100g. The number of food items classified as canned is 1 item. The highest amount of calcium from the 1 canned items is in Squash, summer, zucchini, italian style, canned where the level is 17.00 mg per 100g.The total food items which are raw is 2 items. The highest amount of calcium from the 2 raw items is in Squash, zucchini, baby, raw where the content is 21.00 mg per 100g. The number of food items which are cooked are 4 items. The highest amount of calcium from the 4 cooked items is in Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt where the amount is 18.00 mg per 100g. Comparing raw and cooked zucchini shows that cooking can change the levels of calcium by 3 mg in a 100g serving.Average Content for zucchini
The average (or more correctly the arithmetic mean) amount of calcium contained in 100g of zucchini, based on the list below of 8 different items under the general description of zucchini, is 17.75 mg of calcium. This average value corresponds to 1.78 % of the recommended dietary allowance (or RDA) in your diet. The averages for the different nutrients are as follows; the average amount of Energy is 18.13 kcal, the average amount of Protein is 1.34 g, the average amount of Total Fat is 0.24 g and the average amount of Carbohydrate is g.Median Amount
The median value of Calcium is found in Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt which in 100g contains 18.00 mg of Calcium. This corresponds to 2 % of the recommended daily allowance. For this serving the amount of Energy is 15.00 kcal, the amount of Protein is 1.14 g, the amount of Total Fat is 0.36 g and the amount of Carbohydrate is 2.69 g.Highest calcium Content per 100g

Using the list below for the 8 different zucchini nutrition entries in our database, the highest amount of calcium is found in Squash, zucchini, baby, raw which contains 21.00 mg of calcium per 100g. The associated percentage of RDA is 2 %. For this 100g serving the Energy content is 21.00 kcal, the Protein content is 2.71 g, the Total Fat content is 0.40 g, the Carbohydrate content is 3.11 g. 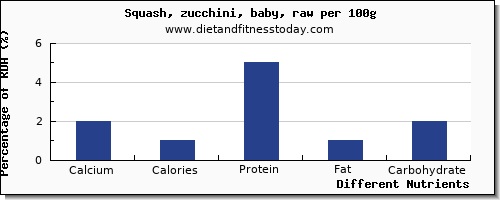
The lowest amount of calcium in 100g is in Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, raw which contains 16.00 mg. This gives as percentage of the recommended daily allowance 2 % of the RDA. For this 100g serving the amount of Energy is 17.00 kcal, the amount of Protein is 1.21 g, the amount of Total Fat is 0.32 g, the amount of Carbohydrate is 3.11 g.
The difference between the highest and lowest values gives a calcium range of 5 mg per 100g. The range for the other nutrients are as follows; 4 kcal for Energy, 1.5 g for Protein, 0.08 g for Total Fat, 0 g for Carbohydrate.
Highest Amount of calcium per Serving
Please remember that the above gives an accurate value in 100g for high calcium foods in your diet. For example 100g of Squash, zucchini, baby, raw contains 21.00 mg of calcium. However, there are other factors to consider when you are assessing your nutritional requirements. You should also take into account portion sizes when you are considering the calcium nutritional content.
The food with the highest calcium content per typical serving is Squash, summer, zucchini, italian style, canned which contains 38.59 mg in 1.000 cup (or 227.00 g). The percentage of the recommended daily value for this serving is 4 %. For this serving the Energy content is 65.83 kcal, the Protein content is 2.34 g, the Total Fat content is 0.25 g and the Carbohydrate content is 15.55 g.
Nutritional Information Summary
From the list below you can find a full nutrition facts breakdown for all foods containing calcium which can be scaled for different servings and quantities. We have also sorted our complete nutritional information and vitamin database of over 7000 foods, to give a list of calcium rich foods.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||